Institute of Tropical Medicine Antwerp
Available courses




In this section you will find general information delivered by ITM's student service.














MID (Molecular Data for Infectious Diseases) is a course for experienced molecular biologists. The course focuses on selection and implementation of appropriate molecular tools for answering clinical and epidemiological questions on infectious diseases in resource-limited settings. The emphasis lies on methods for diagnosing and characterizing viruses, bacteria, parasites, and vectors.

This page contains general info about the MPH2324-programme, valid and applicable throughout the full academic year.




This short course offers essential clinical and biomedical knowledge on diseases and health problems that occur in (sub)tropical settings and in vulnerable life stages (for example childhood or vaccine-preventable diseases), or other vulnerable settings (for example epidemics or migration). This course is an introduction for health professionals who lack exposure to these conditions or lack prior training.
Public health knowledge and skills to deal with these health problems in an international context are part of the course “Challenges in International Health” (CIH).
The course is offered in a “blended” format, with interactive online self-paced study material, and real time seminars (preferably face-to-face but online attendance is possible, once a week on Friday morning).At the end of this course, you should be able to:
· Describe the essential biomedical and clinical aspects of the main tropical, infectious, vaccine-preventable diseases, and non-communicable diseases, in terms of care, prevention, and control.
· Determine the causes, symptoms and preventive measures of the main epidemic-prone diseases;
· Explain the health problems specific to newborn babies and children.
· Discuss the integrated management of specific health problems affecting children and newborns, including undernourishment
· Identify the specific challenges of laboratory diagnostics in low-resource environments.
· Work independently
· Communicate and collaborate in a multidisciplinary and multicultural environment
· Developing continuous learning skills


Here should describe the overall course goals and scope

The course component 4 "Health in Vulnerable Situations" is designed to empower healthcare professionals with the knowledge, skills, and perspectives necessary to address the multifaceted challenges faced by individuals and communities in vulnerable situations. In this course, we focus on vulnerability related to with sexual and HIV health issues, maternal health, and child health. By adopting a comprehensive and integrated approach, the course aims to contribute to improved health outcomes and reduced disparities.
Clinicians, nurses, midwives and allied health professionals play a significant role in ensuring the promotion of reproductive, sexual, maternal and child health. You will focus on the specific needs of groups in vulnerable stages of their life-course, including children, adolescents and pregnant women. In addition, you will understand how and why key populations such as men who have sex with men or sex workers, face multiple vulnerable situations. You will learn how to critically assess sexual and reproductive health problems and how to develop an action plan to address priorities in a particular local health system. You will get an in-depth perspective of the challenges to organise combination HIV prevention and a tailored integrated programme approach for children and neonates and their families.
The overall goal is to introduce students to a range of understandings of vulnerabilities which have impacts on health and well-being. We accomplish this goal by following across the life-course using the continuity of sexual, reproductive, maternal and child life stages. In each stage, we identify and analyze the main causes of vulnerability (including biological, socio-economic, all forms of discrimination, gaps in evidence and clinical care provision, health systems) and apply a health system perspective to addressing them. We make extensive use of the case study method to demonstrate practical approaches to addressing vulnerability (of people, populations, situations and health systems), using a range of countries.


This CIH course component is an introduction to concepts and methods to analyse health problems, interventions and health programmes. This analysis helps to understand the importance of the problem, its burden and its determinants. The theoretical aspects of four main intervention strategies: vector control; screen, test and treat; vaccination strategies; and behavioural interventions, are discussed whether applied as a preventive, curative or rehabilitative concept. Some current operational challenges in the prevention and control of key health problems are touched upon. Concepts taught in the first two weeks will be applied in the context of an outbreak, both in outbreak investigation and outbreak mitigation.
The concepts, analytical frameworks, and implementation strategies are illustrated through applications in a wide range of health problems: tuberculosis, malaria, measles, hepatitis B, leishmaniasis, mpox, diabetes, yellow fever and COVID-19. The focus is on low- and middle-income countries, but also other contexts of high-income countries are included.
The overall goal of the course "Health Problems: From Prevention to Control" is to empower students with a comprehensive understanding of health challenges and equip them with the knowledge, skills, and ethical awareness needed to make meaningful contributions to the prevention, management, and control of health problems, thereby promoting individual and community well-being.
By the end of course component 1 (CC1), you are expected to have a comprehensive understanding of various health issues and get the knowledge and skills to effectively prevent, plan interventions, and control them.
You should specifically be able to:
Describe the importance/burden of a particular health problem in terms of frequency, severity, inequity and economic cost and compare it with the importance of other health problems
Determine different stages of health problem/disease evolution, their (social) determinants, transmission modes (for communicable diseases)
Explain the link between epidemiological model, risk factors and intervention approaches
Indicate the importance of implementation challenges in the prevention and control of key health problems, such as acceptability, identification of target groups, community and patient involvement
Describe the four main public health intervention strategies in terms of effectiveness: vector control, vaccination, test & treat, and behavioural change strategies
Identify theoretically possible intervention strategies - ranging from health promotion, disease prevention and control, and curative care – that can reduce the burden at individual and/or population level caused by a particular health problem
Detect an outbreak, based on epidemiological data
Identify steps of an outbreak investigation
Describe an outbreak in terms of time, place, person
Define and plan an appropriate outbreak response
Communicate findings of an outbreak investigation

The
overarching learning objectives of this course include:
- Identification of the challenges that
climate change poses to global health.
- Definition and delineation of the
challenges confronting vulnerable populations in times of crisis.
- Exploration and evaluation of
potential solutions for health-related issues arising in the context of crises.
- Application of scientific
methodologies to proactively anticipate and address future health-related
challenges faced by populations.
These objectives form the foundation upon which this course is built, fostering a comprehensive understanding of health issues and crises catalysed by climate change and related factors.
Generic competencies:
- Search information in relevant sources from different disciplines
- Critically assess data & findings in literature and other sources
- Interpret, summarise & present information orally and graphically
This short course offers essential clinical and biomedical knowledge on diseases and health problems that occur in (sub)tropical settings and in vulnerable life stages (for example childhood or vaccine-preventable diseases), or other vulnerable settings (for example epidemics or migration). This course is an introduction for health professionals who lack exposure to these conditions or lack prior training.
Public health knowledge and skills to deal with these health problems in an international context are part of the course “Challenges in International Health” (CIH).
The course is offered in a “blended” format, with interactive online self-paced study material, and real time seminars (preferably face-to-face but online attendance is possible, once a week on Friday morning).At the end of this course, you should be able to:
· Describe the essential biomedical and clinical aspects of the main tropical, infectious, vaccine-preventable diseases, and non-communicable diseases, in terms of care, prevention, and control.
· Determine the causes, symptoms and preventive measures of the main epidemic-prone diseases;
· Explain the health problems specific to newborn babies and children.
· Discuss the integrated management of specific health problems affecting children and newborns, including undernourishment
· Identify the specific challenges of laboratory diagnostics in low-resource environments.
· Work independently
· Communicate and collaborate in a multidisciplinary and multicultural environment
· Developing continuous learning skills




LeiShield Molecular Epidemiology is a self-study course suite developed by ITM Antwerp, for exchange students of the LeiShield-MATI project.
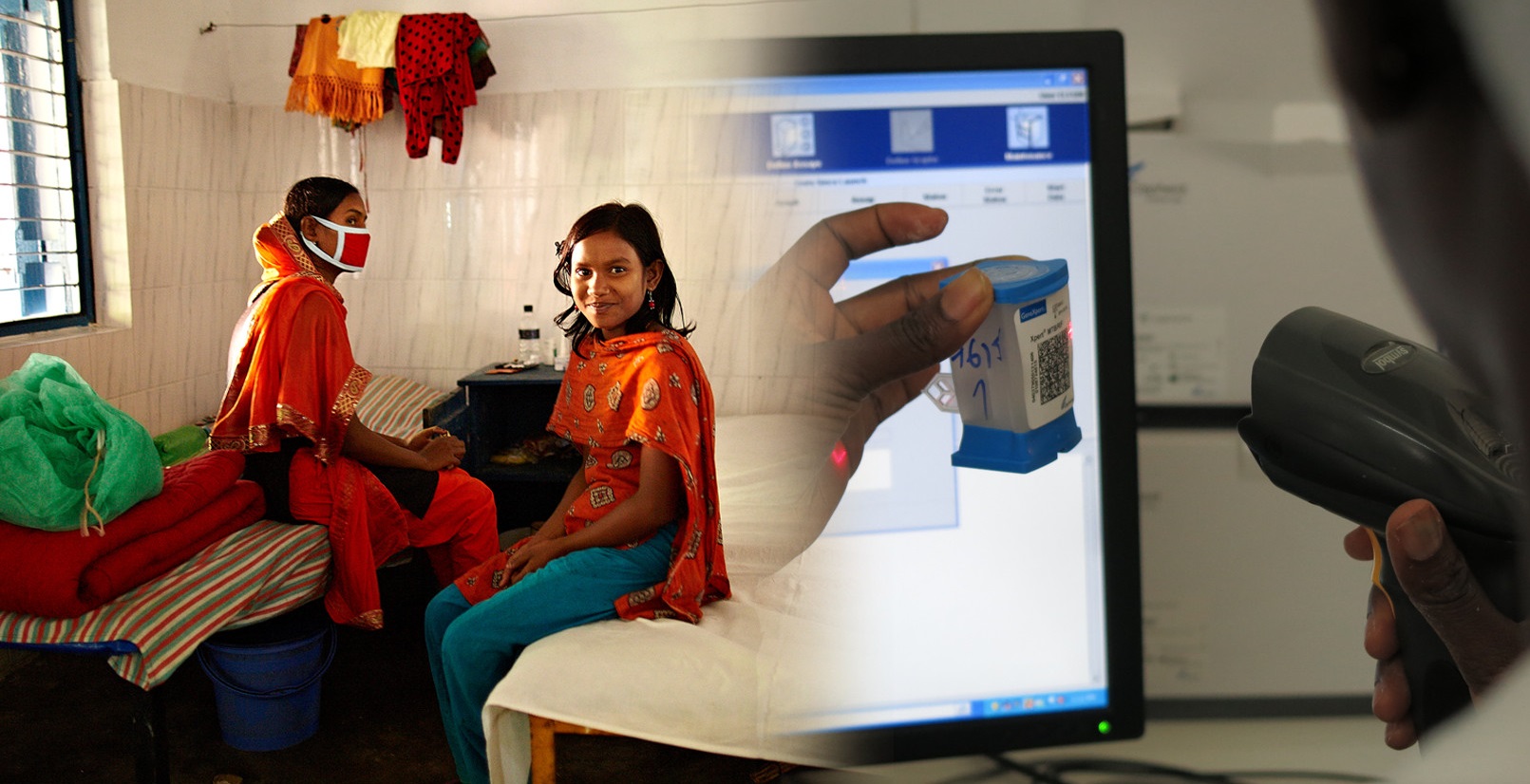
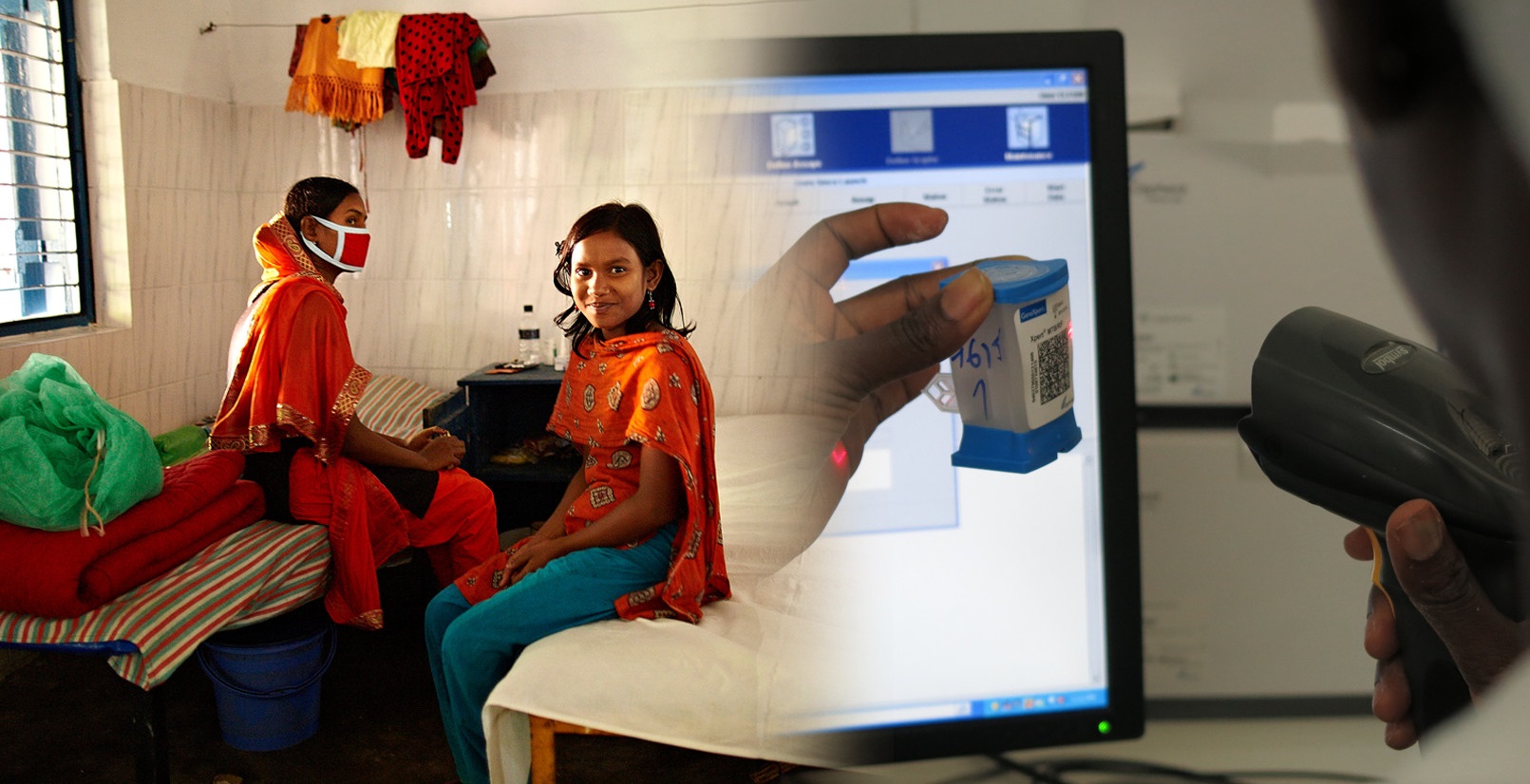




Introduction
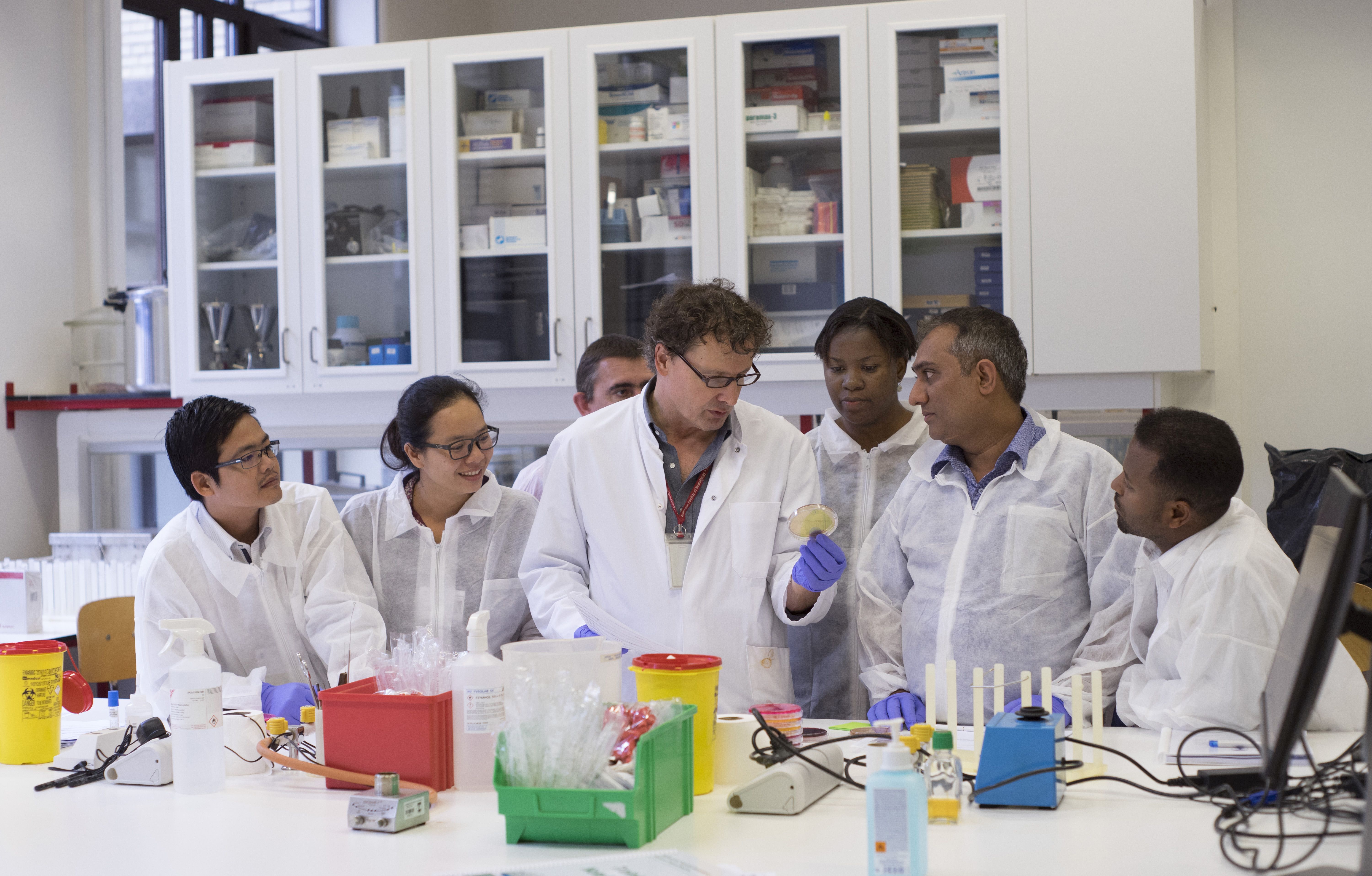
FiMAB is an international training programme by the Institute of Tropical Medicine and VLIR-UOS (Belgium) that supports the implementation of targeted NGS AmpliSeq assays to strengthen malaria molecular surveillance (MMS) that can guide national control programmes. Through F2F laboratory- and bioinformatic training at the Institute of Tropical Medicine (Antwerp) planned in 2024, young academics of around the globe become familiar with MMS as a key activity to monitor transmission, sources of epidemics and the emergence and spread of drug resistant mutations in the parasite. To provide applicants in background on the subject, we created this digital classroom for the year 2023, which will be used to asses individual progress and participation, one crucial element to be selected for the F2F trainings.
In concert with partners in South-America, Africa and Southeast Asia the Malariology unit at ITM has built on sequencing capacity and a surveillance network with leading public health institutions. To this end, the courses aim to transfer knowledge to potential partners in the South and broaden the global alliance by supporting young academic graduates in endemic countries, our Actors of Change.
What to do?
Below, you can find 4 courses that cover the topics necessary for correct understanding of AmpliSeq. You must learn all, because when using a novel technique it is necessary to identify the field in which it is applied. For this purpose, we go through the challenges in malaria research, the underlying mechanisms, and how AmpliSeq can provide a solution that contributes to the fight against malaria.
How to do?
To complete a course, each participant must go through all content. Be aware, that sometimes you'll need to click on images and read pop-ups & subscripts carefully to access all content. When you think you master the course material, go and proceed to the exercises that are at the end of each topic. Each exercise covers open and closed questions, multiple choice, and will be used to grade your participation, motivation and knowledge. Based on these three aspects, people are invited to the F2F Courses organized at ITM, Antwerp in Belgium 2024.
LETS GET THIS PARTY STARTED!
Students will learn how to write a research proposal for their thesis topic in the context of selected
tropical diseases. The main activity is focussed on the development of the thesis project supported
by active discussions of different sections of their research by peers and teaching staff. These activities
will additionally be supported by lectures and self-directed learning.
The module accounts for 10 ECTS which are divided over two blocks of 5 ECTS: Research methodology
and Biomedical Methods I.
This is the page for the MPH2223 Trial Exam, to get acquainted with the functionalities of Moodle within an "Exam environment".
This page will be opened and accessible as of Wed. 09-Nov-2022, 14h15 PM CET.

This is a demo course to show you all kinds of learning activities that you can implement on Moodle
hfdqlskdjflqkjsdlfkqnldfnqlksfnlksjflkjqlmdksjfpozqiepotioqmzjflknzqknd;snfkqs,lkfjqlkzjfls

